Characterization and conservation of bioresources of Himalaya
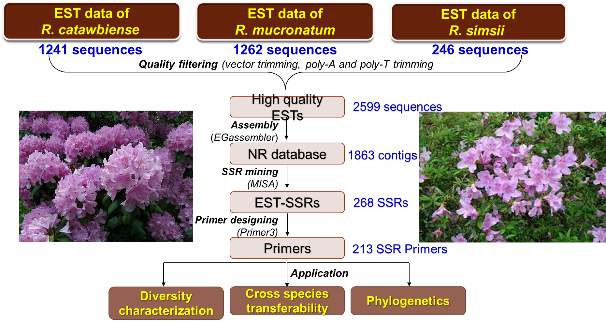
The Eastern Himalayas, a globally recognized biodiversity hotspot, represent a rich biodiversity. The harnessing of this immense bio-wealth is crucial towards sustainable development and human well-being. A comprehensive approach to this challenge goes beyond traditional conservation methods and integrates cutting-edge scientific techniques with community engagement. The plant used in traditional medicine by local communities having tremendous therapeutic potential. The scientific validation of this knowledge has been validated by characterization and identification of active molecules and their quantification using advanced analytical techniques. Modern techniques like network pharmacology approaches have been applied for drug discovery in wild edible fruit and medicinal plant species and other medicinal plants of the Himalayan region. The foundation of any robust conservation and utilization strategy for bioresources lies from species to genetic characterization. Molecular and genetic characterization have been selected as tools to understand the unique genetic identity and diversity of a species using genetic markers, and elite and vulnerable populations/ germplasm have been identified and prioritize for cultivation and conservation in species like Rhododendron, Hedychium spicatum and other species. Furthermore, genomic resources that involves building comprehensive databases of genomic and genetic information, and genetic markers for species like Hedychium spicatum, Rhododendrons, etc has been performed.
These resources are a powerful tool for quality determination in these species. For rare, endangered, or slow-growing species of the Eastern Himalayas, tissue culture creates of large numbers of disease-free, genetically identical plantlets without harvesting from the wild, thus alleviating pressure on natural populations. A key approach adapted includes developing robust tissue culture propagation protocols for commercially important medicinal and aromatic plants and protocols have been developed for threatened Rhododendrons and rare and endangered orchid species. However, the real-world impact of these protocols hinges on their implementation. The training programs are comprehensive, covering everything from nursery management and planting techniques to sustainable harvesting practices and post-harvest processing. This knowledge transfer not only enables farmers to cultivate high-demand medicinal plants for commercial purposes but also provides them with a sustainable and lucrative alternative to over-harvesting from the wild.
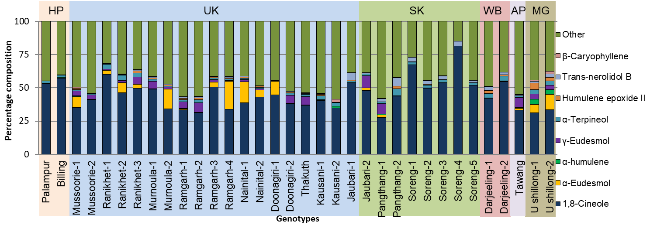
Chemical profiling of medicinal plants of Himalaya